In vitro Assays and Techniques
- Cis-Bio Fluorescent ligand displacement assays (measured in 384-well format using Flexstation 3).
- Radioligand binding assays for opioid receptors (In 96-well format)
- Promega GloSensor cAMP assay (measured in 384-well format using Synergy4 and Flexstation 3).
- DiscoverX pathhunter β-arrestin 1 and 2 recruitment assays for delta opioid receptors and β-arrestin 2 recruitment for mu opioid receptors and for kappa opioid receptors (measured in 384-well format using Synergy4 and Flexstation 3).
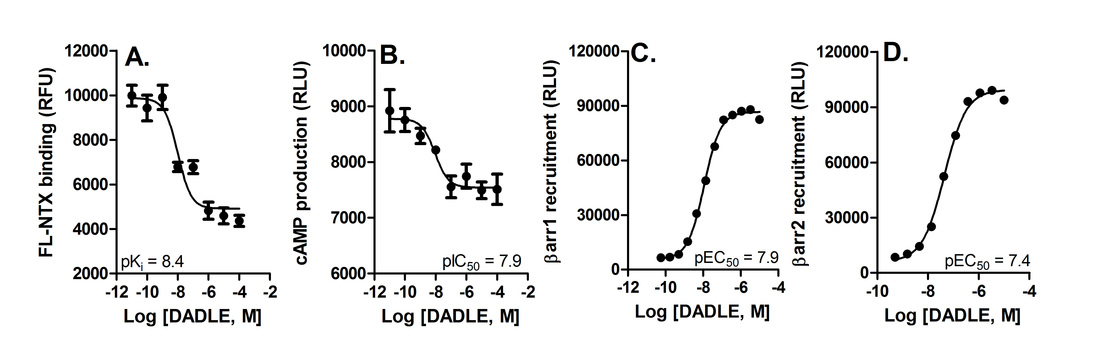
Figure: Pharmacological characterization of the DOR agonist DADLE. A. Displacement of fluorescent naltrexone. B, Inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP. C, Recruitment of β-arrestin1. D, Recruitment of β-arrestin1 by DADLE.
- Heterodimer calcium mobilization screening assay (measured in 384 well format using Flexstation 3 using FLIPR6 calcium assay kit from Molecular Devices ).
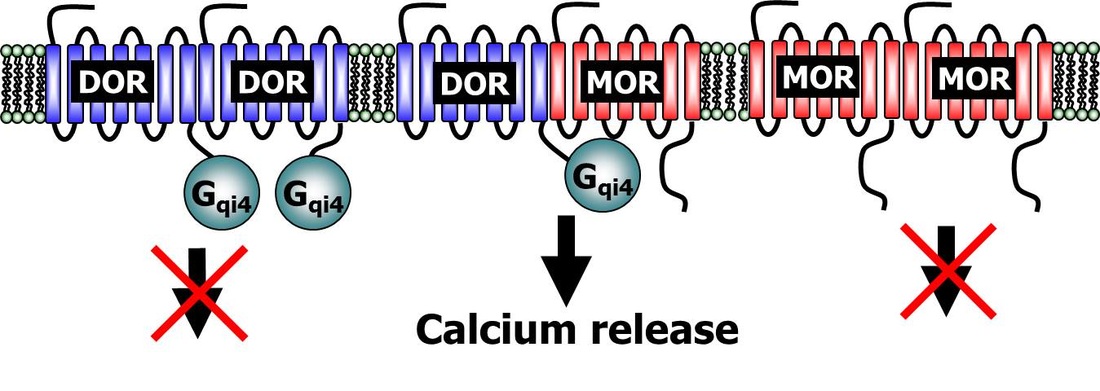
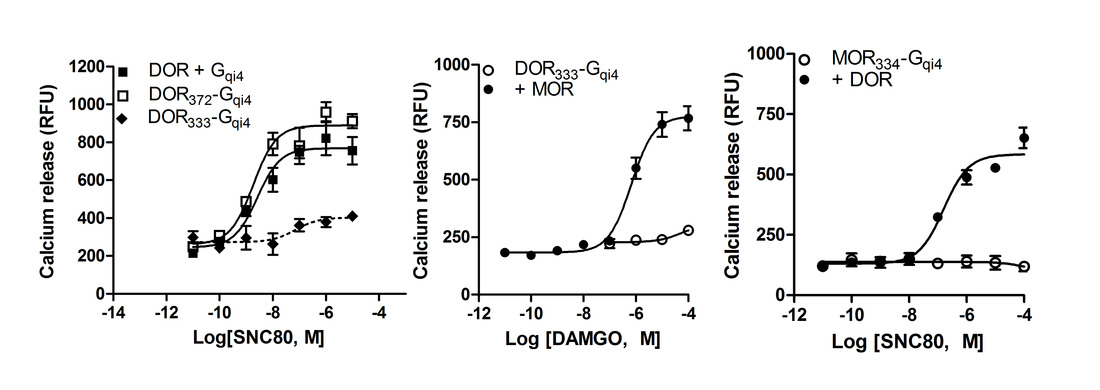
Figure: Heteromer selective assay for Gi-coupled (and Gs-coupled) receptors. Fusing A chimeric Gqi4 (or Gqs4) protein to a truncated GPCR like the delta opioid receptor (DOR) prevents calcium signaling from the delta opioid receptor homomers. co-expression of a Gi- or Gs-coupled wild-type receptor, like the mu opioid receptor (MOR) can rescue calcium signaling through the chimeric protein. Importantly, homomers of the wild-type receptor are unable to induce calcium signaling as it signals through Gi or Gs and there is no free Gqi4.
- Point mutagenesis, introducing of tags, cloning of fusion proteins.
- Digital fluorescence microscopy for imaging receptor signaling and trafficking (using a Iris digital fluorescence microscope).
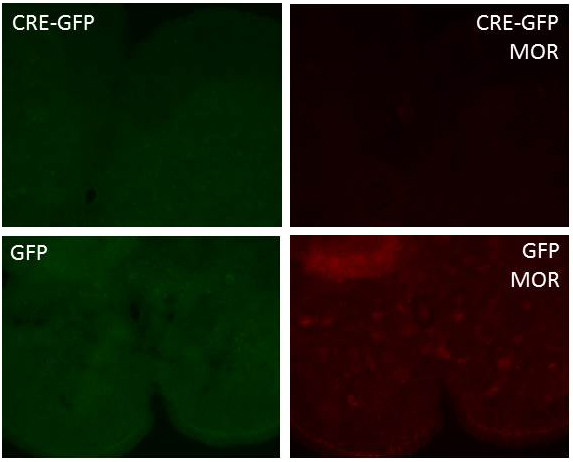
Figure: Viral knockdown of spinal mu opioid receptors (MOR) in conditional floxed MOR C57BL/6 mice. Floxed MOR mice were intra-thecally injected with AAV-GFP or AAV-CRE-GFP. Mice were perfused three weeks after injection and imaged for viral infection at 488nm. Mu opioid receptor expression was detected following immunostaining with a primary rabbit anti-MOR antibody (Immunostar, #24216) and a secondary goat anti-rabbit alexa594 antibody.
- Production of lentivirus using pLENTI system (Life Technologies)
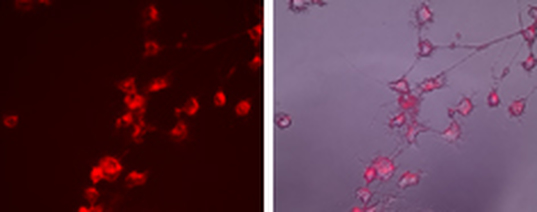
Figure: Lentivirus driven expression of Beta-arrestin2-cherry in NG108-15 cells. NG108-15 cells endogenously expressing delta opioid receptors were infected with lentivirus containing beta-arrestin2-cherry. The lentivirus was produced using the virapower system with the beta-arrestin2-cherry expression behind a CMV promotor.
- Protein analysis using western blot, ELISA and real time qPCR (using a Viia 7 system)
In vivo assays and techniques
- Thermal analgesia using a Radiant heat tailflick apparatus (Columbus instruments) or Hot plate (Columbus instruments).
- Models for opioid dependence and tolerance.
- Mechanical analgesia using Von Frey filaments.
- Models for alcohol withdrawal induced hyperalgesia.
- Alcohol induced Loss of Righting Reflex (LORR).
- Models for anxiety-like behavior using dark light transition boxes (Med associates) and elevated zero maze (Clever Sys).
- Models for depression-like behavior using Tail suspension boxes (Med associates) and Forced swim recorded by videotracking software.
- Barnes maze for hippocampal dependent learning
- 2-bottle choice self-administration using double grommet animal cages (Allen town).
- Induction of inflammatory pain using complete Freund’s Adjuvant.
- Induction of drug place preference or aversion using 2-chamber conditioned place preference inserts into locomotor activity boxes (Med associates).
- Stereotactic infusion and cannulation of mice (using a KOPF 1900 digital stereotax).
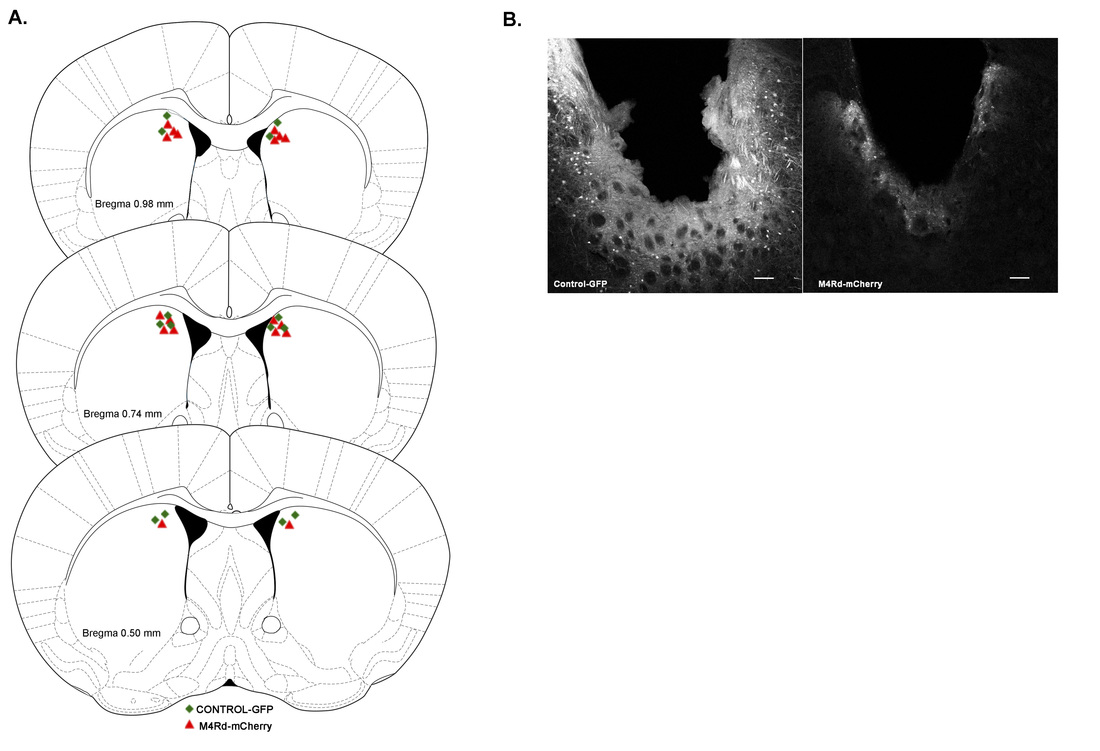
Figure: Viral infusion of AAV-GFP or AAV-M4Rd/cherry into the dorsal striatum of C57BL/6 mice using steraotactic surgery.